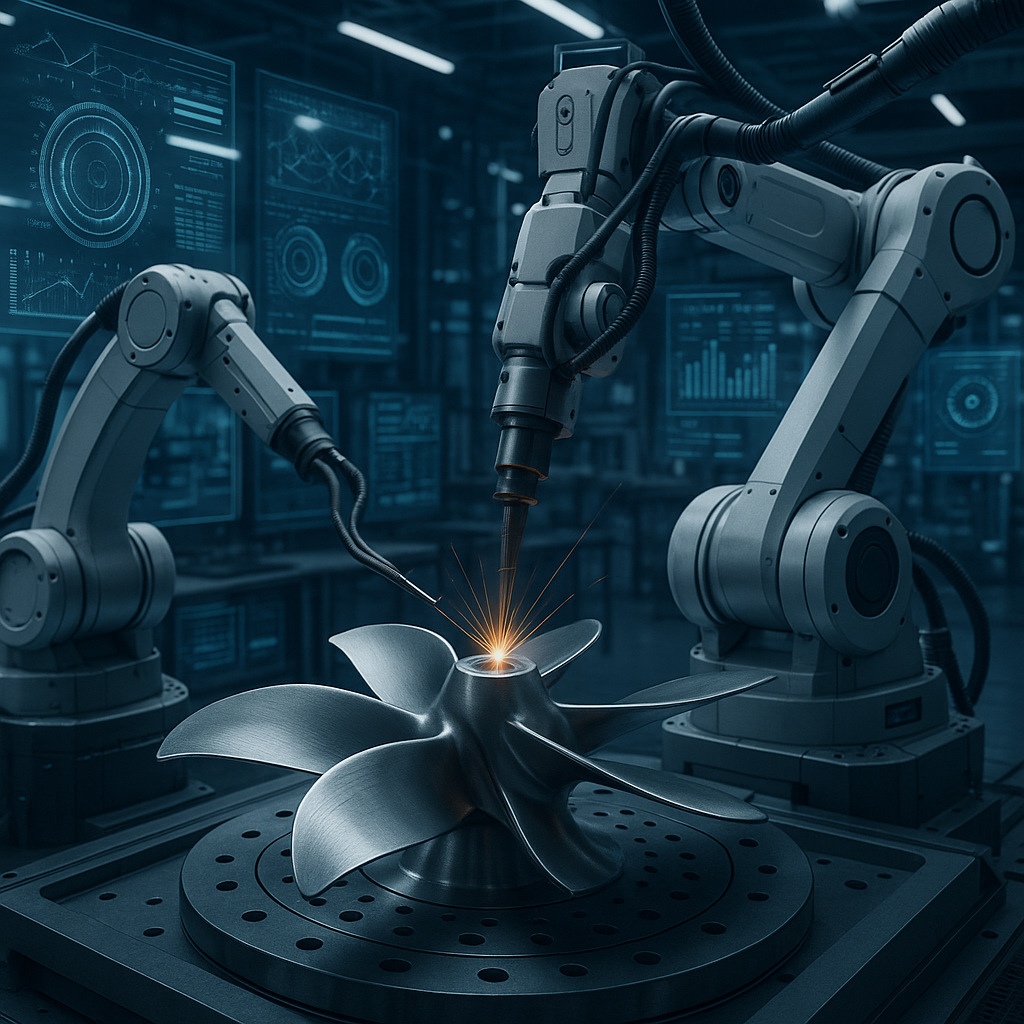
What Happened
Arizona State University has recently advanced the frontier of metal additive manufacturing by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with 5-axis 3D printing technology to produce mission-critical items such as propellers. This innovative approach was highlighted in a June 2025 report by ASU (Using AI for smarter metal 3D printing of mission-critical items like propellers). The project leverages the capabilities of 5-axis additive manufacturing, allowing for complex geometries and improved mechanical properties, while AI algorithms optimize the printing process for enhanced part quality and reduced production time.
Why It Matters
The manufacturing of mission-critical components such as propellers demands exceptional precision, structural integrity, and reliability. Traditional manufacturing methods for such parts are often costly, time-consuming, and limited in design flexibility. The integration of AI with 5-axis metal 3D printing addresses these challenges by enabling the production of complex, high-performance parts with fewer defects and optimized material properties.
This development is significant because it demonstrates the potential to transform industries reliant on metal components with intricate geometries and stringent performance requirements, including aerospace, marine, and energy sectors. By reducing lead times and enhancing part quality, this technology could lead to safer, more efficient propulsion systems and other critical machinery.
Technical Context
5-axis 3D printing refers to additive manufacturing using a print head or build platform that can move along five different axes simultaneously, beyond the conventional three linear axes (X, Y, Z). This multi-axis capability enables non-planar printing paths, allowing for continuous layer deposition on complex surfaces and reducing the need for support structures. The technology supports printing on curved or angled surfaces, which is particularly advantageous for parts like propellers with aerodynamic shapes.
When combined with AI, the system can dynamically adjust printing parameters such as laser power, scan speed, and deposition paths in real time. AI algorithms analyze sensor data and part geometry to optimize the process, minimizing defects like porosity and residual stress while ensuring dimensional accuracy. This closed-loop control represents a significant advancement over traditional fixed-parameter printing.
While the exact AI models and sensor integration details from ASU’s project are not fully disclosed, the approach likely involves machine learning techniques trained on extensive datasets to predict optimal printing conditions for different geometries and materials.
Near-Term Prediction Model
Given the current R&D status of AI-enhanced 5-axis metal 3D printing at Arizona State University, the technology is expected to transition to pilot-scale applications within the next 12 to 24 months. Early adopters in aerospace and marine propulsion manufacturing may begin integrating pilot systems to validate performance and cost benefits.
Commercial deployment at scale could follow within 3 to 5 years, contingent on further refinements in AI algorithms, hardware robustness, and regulatory approvals for mission-critical parts. The impact score for this technology is high, estimated at 80 out of 100, due to its potential to disrupt traditional manufacturing and improve part performance significantly. Confidence in this timeline is moderate (around 70) given typical challenges in scaling advanced manufacturing processes.
What to Watch
- Progress in AI model transparency and real-time sensor feedback integration to enhance adaptive control during printing.
- Development of standardized testing protocols and certification pathways for mission-critical 3D printed metal parts.
- Collaborations between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies to accelerate adoption and ensure safety compliance.
- Expansion of multi-axis printing hardware capable of handling larger build volumes and diverse metal alloys.
- Cost-benefit analyses comparing AI-driven multi-axis printing with traditional manufacturing for complex metal components.
In conclusion, Arizona State University’s pioneering work combining AI with 5-axis metal 3D printing marks a significant milestone in additive manufacturing. By enabling smarter, more precise fabrication of complex mission-critical parts like propellers, this technology promises to reshape advanced manufacturing landscapes in the near future.