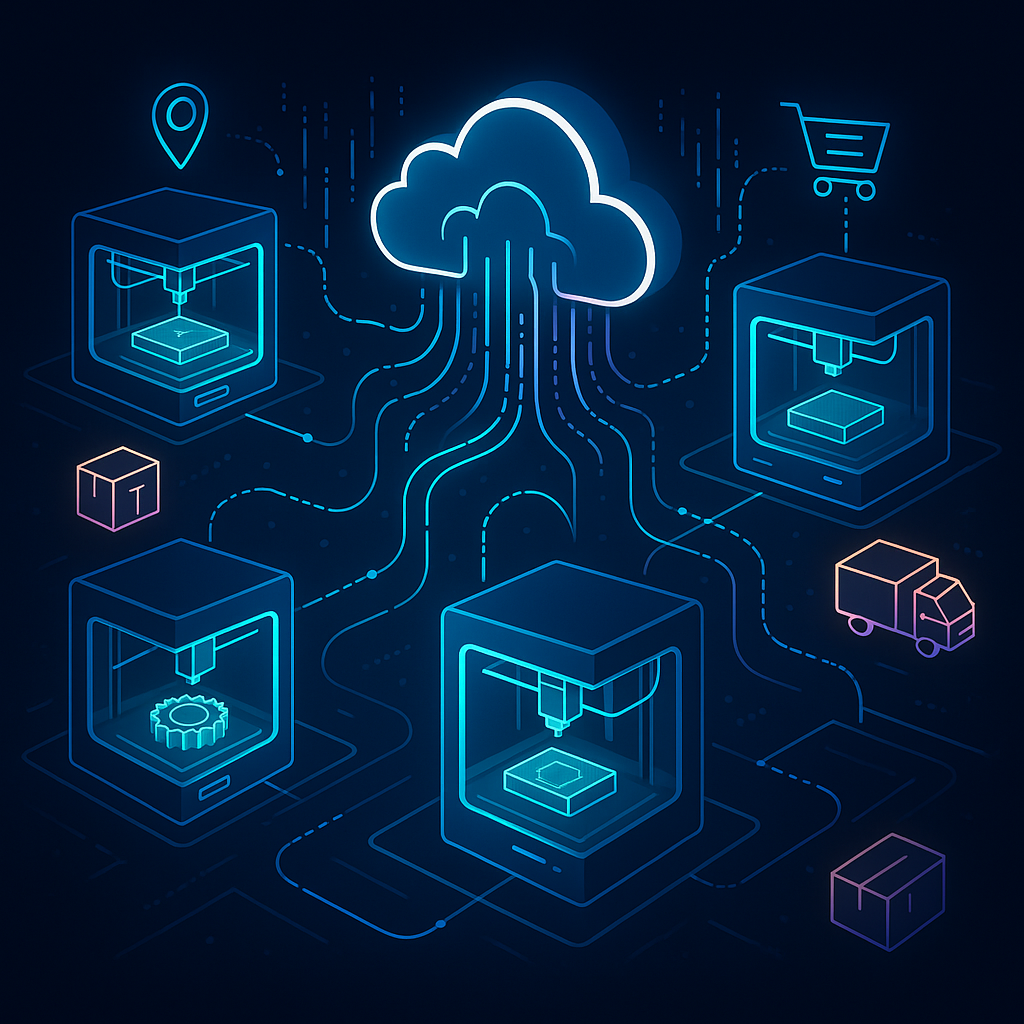
What Happened
Recent developments in distributed manufacturing are increasingly influencing the landscape of digital inventory and on-demand 3D printing. According to a recent article from 3D Printing Industry, the integration of distributed manufacturing techniques with digital inventory strategies is becoming a pivotal trend. This approach decentralizes production, enabling manufacturers to store digital files rather than physical goods and produce items on-demand closer to the point of use.
Why It Matters
The shift towards distributed manufacturing combined with digital inventory offers transformative potential for supply chains and production models. It reduces the need for large physical inventories, decreases shipping costs and lead times, and enhances responsiveness to customer demand fluctuations. This can be especially critical in sectors with high customization needs or volatile demand, such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive industries.
Moreover, distributed manufacturing can improve sustainability by lowering carbon footprints associated with logistics and reducing waste through precise production volumes. The ability to produce parts locally also mitigates risks related to global supply chain disruptions, a lesson reinforced by recent worldwide events.
Technical Context
Distributed manufacturing leverages additive manufacturing technologies—primarily 3D printing—to fabricate components directly from digital files stored in a digital inventory. This requires robust digital infrastructure for secure file management, standardized data formats, and reliable quality control mechanisms across distributed sites.
Key technical enablers include advanced slicing software that optimizes print jobs for various printers, cloud-based platforms that facilitate file sharing and version control, and integrated IoT devices that monitor printer status and environmental conditions to ensure consistent output quality.
However, challenges remain in ensuring intellectual property protection, maintaining uniform quality standards across geographically dispersed sites, and integrating these systems with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and supply chain management (SCM) tools.
Near-term Prediction Model
Within the next 12 to 24 months, distributed manufacturing combined with digital inventory is expected to transition from pilot and early commercial stages into broader adoption, particularly in industries with complex supply chains and high customization demands. Investment in cloud infrastructure and cybersecurity will accelerate, addressing critical barriers to adoption.
Manufacturers will increasingly deploy regional micro-factories equipped with advanced 3D printers capable of producing end-use parts on-demand, reducing dependency on centralized warehouses. Software platforms that integrate digital inventory management with production scheduling and quality assurance will mature, enabling seamless workflows.
Despite these advances, widespread adoption may be tempered by regulatory considerations, the need for workforce training, and the time required to validate distributed production for safety-critical applications.
What to Watch
- Development of standardized protocols and certifications for distributed 3D printing quality assurance.
- Emergence of secure digital rights management (DRM) solutions to protect intellectual property in digital inventory systems.
- Integration of AI-driven analytics for predictive maintenance and production optimization in distributed manufacturing networks.
- Adoption rates of cloud-based digital inventory platforms by small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- Regulatory frameworks evolving to accommodate decentralized manufacturing models, especially in medical and aerospace sectors.
- Collaborations between logistics providers and distributed manufacturing hubs to streamline last-mile production and delivery.
While specific implementation details and case studies remain limited in the public domain, ongoing reporting from industry sources like 3D Printing Industry will be essential to monitor ongoing progress.